تحليل سينماتيكي و رفتار مكانيكي مواد مدل شده بر اساس فرضيه محيط هاي پيوسته را مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته (Continuum Mechanics) مي نامند. در درس مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته، علاوه بر فرضيه بنيادين پيوستگي مواد، دو محدوديت ديگر را روي اجسام در نظر مي گيريم:
- اولا الزام مي كنيم كه مواد همگن باشند، يعني خواص مكانيكي يكسان در تمام موقعيت ها داشته باشند.
- ثانيا بطور كلي موادي را در نظر مي گيريم كه همسانگرد هستند، يعني در يك نقطه داراي خواص فيزيكي يكسان در هر جهت مي باشند...
مجموعه آموزشي مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته براي مهندسين توماس ميس، يكي از مجموعه كتاب هاي مرجع و كاربردي در زمينه مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته است كه در اكثر دانشگاه هاي ايران تدريس مي گردد. در اين مجموعه آموزشي شما قادر خواهيد بود اولا نسخه اصلي كتاب به زبان لاتين (Introduction to Continuum Mechanics)، ثانيا نسخه ترجمه شده اين كتاب به زبان فارسي (مترجم دكتر عباس راستگو)، ثالثا تشريح كامل مسائل اين كتاب را بطور كامل دانلود نماييد.

كتاب مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته براي مهندسين،
مشتمل بر 440 صفحه، در 9 فصل، با فرمت PDF، به زبان فارسي، همراه با تصاوير به ترتيب زير گردآوري شده است:
فصل 1: نظريه محيط هاي پيوسته
- مفهوم محيط هاي پيوسته
- مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته
فصل 2: رياضيات ضروري
- عددها، بردارها و تانسورهاي قائم
- تانسور جبري در نمادگذاري نمادين، قرارداد جمع
- نمادگذاري شاخصي
- ماتريس ها و دترمينان ها
- انتقال ماتريس هاي قائم
- مقادير اصلي و جهت هاي اصلي تانسورهاي متقارن مرتبه دوم
- ميدان هاي تانسوري، حسابان تانسورها
- نظريه هاي انتگرالي گوس و استوكس
- مسائل
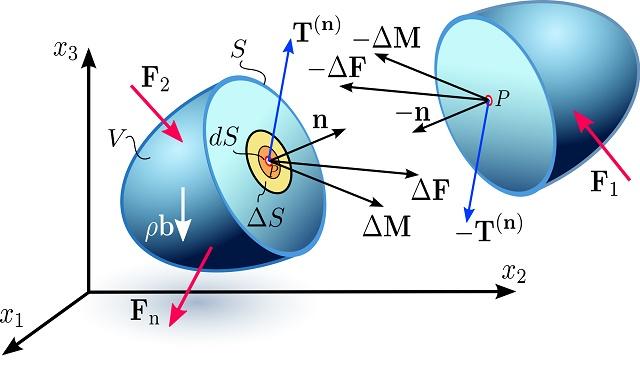
فصل 3: اصول تنش
- نيروهاي حجمي و سطحي، چگالي جرم
- اصل تنش كوشي
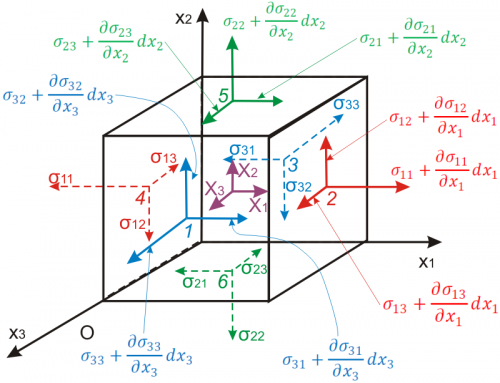
- تانسور تنش
- تعادل نيرو و ممان، تقارن در تانسور تنش
- قوانين انتقال تنش
- تنش هاي اصلي، جهت هاي تنش اصلي
- مقادير تنش حداقل و حداكثر
- دايره هاي مور براي تنش
- تنش صفحه اي
- بيان تنش كروي و بيان تنش انحراف
- تنش برشي هشت وجهي
- مسائل
فصل 4: سينماتيك تغير شكل و حركت
- ذرات، پيكربندي ها، تغير شكل و حركت
- مختصات مادي و فضايي
- توصيف هاي اولري و لاگرانژي
- ميدان تغير مكان
- مشتق مادي
- گراديان تغير شكل، تانسورهاي كرنش محدود
- نظريه تغير شكل بسيار كوچك
- نسبت هاي كشيدگي
- تانسور چرخش، تانسورهاي كشيدگي
- گراديان سرعت، نرخ تغير شكل، گردابي
- مشتق مادي اجزاء خطي، مساحت ها، حجم ها
- مسائل
فصل 5: قوانين و معادلات بنيادين
- قوانين تعادل، معادلات ميدان، معادلات اساسي
- مشتقات مادي انتگرال هاي خط، سطح و حجم
- اصل بقاي جرم، معادله پيوستگي
- اصل مومنتوم خطي، معادلات حركت
- تانسورهاي تنش پيلا كرشوف، معادلات لاگرانژ حركت
- اصل ممان اندازه حركت (اندازه حركت زاويه اي)
- اصل بقاي انرژي، معادله انرژي
- آنتروپي و معادله كلازيوس دوهام
- محدوديت هايي بر مواد الاستيك بوسيله قانون دوم ترموديناميك
- تغير ناپذيري
- محدوديت هاي اعمال شده بر معادله هاي اساسي بواسطه تغير ناپذيري
- معادلات اساسي
- مسائل
فصل 6: الاستيسيته خطي
- الاستيسيته، قانون هوك، انرژي كرنشي
- قانون هوك براي مواد همسانگرد، ثابت هاي الاستيك
- تقارن الاستيك، قانون هوك براي مواد غير همسانگرد
- الاستو الاستيك و الاستو ديناميك همسانگرد، اصل جمع آثار
- الاستيسيته صفحه اي
- تابع تنش ايري
- پيچش
- الاستيسيته سه بعدي
- مسائل
فصل 7: شاره هاي كلاسيك
- تانسور تنش چسبنده، شاره هاي استوكسي و نيوتني
- معادلات اصلي جريان چسبنده، معادلات ناوير استوكس
- شاره هاي ويژه
- جريان يكنواخت، جريان غير چرخشي، جريان پتانسيل
- معادله برنولي، قضيه كلوين
- مسائل
فصل 8: الاستيسيته غير خطي
- روش مولگولي براي الاستيسيته لاستيك
- تئوري انرژي كرنشي براي الاستيسيته غير خطي
- حتالت هاي خاص انرزي كرنشي
- حل دقيق براي يك ماده تراكم ناپذير و نئو هوكين
- مسائل
فصل 9: ويسكو الاستيسيته خطي
- مقدمه
- معادلات اساسي ويسكو الاستيك در شكل اپراتور ديفرانسيل خطي
- تئوري يك بعدي، مدل هاي مكانيكي
- خزش و وارفتگي
- اصل برهم نهي، انتگرال هاي توارثي
- بارگذاري هاي هارمونيك، مدول مختلط، مطلوبيت مختلط
- مسائل سه بعدي، اصل تطابق
- مسائل

كتاب مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته براي مهندسين (Continuum Mechanics for Engineers)،
مشتمل بر 400 صفحه، در 9 فصل، با فرمت PDF، به زبان انگليسي، همراه با مسائل به ترتيب زير گردآوري شده است:
- Chapter 1: Continuum Theory
- Chapter 2: Essential Mathematics
- Chapter 3: Stress Principles
- Chapter 4: Kinematics of Deformation and Motion
- Chapter 5: Fundamental Laws and Equations
- Chapter 6: Linear Elasticity
- Chapter 7: Classical Fluids
- Chapter 8: Nonlinear Elasticity
- Chapter 9: Linear Viscoelasticity

كتاب تشريح كامل مسائل مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته براي مهندسين،
مشتمل بر 220 صفحه، با فرمت PDF، به زبان فارسي، كليه مسائل كتاب بالا را بطور كامل تشريح نموده است و به ترتيب زير گردآوري شده است:
- رياضيات ضروري
- اصول تنش
- سينماتيك تغير شكل و حركت
- قوانين و معادلات بنيادين
- الاستيسيته خطي
- شاره هاي كلاسيك
جهت دانلود مجموعه آموزشي مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته به همراه تشريح كامل مسائل، برلينك زير كليك نماييد.
مجموعه آموزشي مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته به همراه تشريح كامل مسائل






 روش هاي اجزاي محدود
روش هاي اجزاي محدود آموزش مقدماتي تا پيشرفته روش هاي عناصر محدود غير خطي
آموزش مقدماتي تا پيشرفته روش هاي عناصر محدود غير خطي مجموعه آموزش روش هاي اجزاي محدود مقدماتي
مجموعه آموزش روش هاي اجزاي محدود مقدماتي روش اجزاي محدود مقدماتي
روش اجزاي محدود مقدماتي برنامه المان چهار گرهي تنش مسطح و كرنش مسطح در نرم افزار MATLAB
برنامه المان چهار گرهي تنش مسطح و كرنش مسطح در نرم افزار MATLAB طراحي قالب تزريق پلاستيك (Injection Mold Design)
طراحي قالب تزريق پلاستيك (Injection Mold Design)