مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته، يك شاخه وسيع از مكانيك محسوب مي شود. هدف اين شاخه علمي، فراگيري اين واقعيت است كه چگونه مسائل مربوط به حركت اجسام شكل پذير (جامد، مايع و گاز) صورت بندي و سئوالات و ايده هاي كلي و حتي مبهم به عبارات دقيق رياضي بدل شوند. در زمينه مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته، كتب متعددي تدوين شده است. كتاب مقدمه اي بر مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته (مايكل لي، ديويد رابين، ارهارد كرمپل) به دو دليل زير به شما علاقمندان پيشنهاد مي گردد:
نخست اينكه سادگي در بيان مطالب، تقسيم بندي مناسب موضوعات، ارائه مثال هاي متعدد براي تفهيم مطلب و گردآوري مسائل زياد در انتهاي هر فصل، كتاب را براي كلاس درس كاملا مناسب نموده است. دوم اينكه با توجه به معرفي تانسورهاي مرتبه دو از طريق تشريح تبديلات خطي، به فهم مبادي رياضي متن كه يكي از پيچيدگي هاي مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته محسوب مي شود، سادگي و سهولت خاصي بخشيده است...
كتاب مقدمه اي بر مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته، يكي از كتاب هاي مرجع و كاربردي در زمينه مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته است كه در اكثر دانشگاه هاي ايران تدريس مي گردد. در اين مجموعه آموزشي شما قادر خواهيد بود اولا نسخه اصلي كتاب به زبان لاتين (Introduction to Continuum Mechanics)، ثانيا نسخه ترجمه شده اين كتاب به زبان فارسي (مترجم دكتر غلامحسين رحيمي)، ثالثا تشريح كامل مسائل اين كتاب را بطور كامل دانلود نماييد.

اين كتاب مشتمل بر 375 صفحه، در 8 فصل، با فرمت PDF، به زبان فارسي، همراه با مسائل به ترتيب زير گردآوري شده است:
فصل 1: مقدمه
- نظريه محيط پيوسته
- محتواي مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته
فصل 2: نمادگذاري شاخصي و تانسورها
- قرارداد جمع، شاخص هاي كاذب
- شاخص هاي آزاد
- دلتاي كرانكر
- نماد جايگشت
- عمليات با نمادگذاري شاخصي
- تانسور، يك تبديل خطي
- مولفه هاي يك تانسور
- جمع تانسور
- حاصلضرب دياديك
- ضرب دو تانسور
- تانسور واحد
- برگردان يك تانسور
- تانسور متعامد
- قوانين تبديل براي مولفه هاي دكارتي تانسورها و بردارها
- تانسورهاي متقارن و پادمتقارن
- بردار دوگان يك تانسور پادمتقارن
- مقادير ويژه و بردارهاي ويژه يك تانسور
- مقادير اصلي و جهات اصلي تانسورهاي متقارن حقيقي
- ماتريس يك تانسور نسبت به جهات اصلي
- پاياهاي عددي يك تانسور
- توابع با ارزش تانسوري يك عددي
- ميدان عددي، گراديان يك تابع عددي
- ميدان برداري، گراديان يك تابع برداري
- اثر يك تانسور مرتبه دو
- ديورژانس يك ميدان برداري و ديورژانس يك ميدان تانسوري
- كرل يك ميدان برداري
- مختصات قطبي
- مسائل
فصل 3: سينماتيك محيط هاي پيوسته
- توصيف حركت يك محيط پيوسته
- توصيف مادي و توصيف فضايي
- مشتق مادي
- يافتن شتاب يك ذره از يك ميدان سرعت داده شده
- تغير شكل
- كرنش اصلي
- اتساع
- نرخ تغير شكل
- معادله بقاي جرم
- شرايط سازگاري براي مولفه هاي بي نهايت كوچك كرنش
- شرايط سازگاري براي مولفه هاي نرخ تغيير شكل
- مسائل
فصل 4: تنش
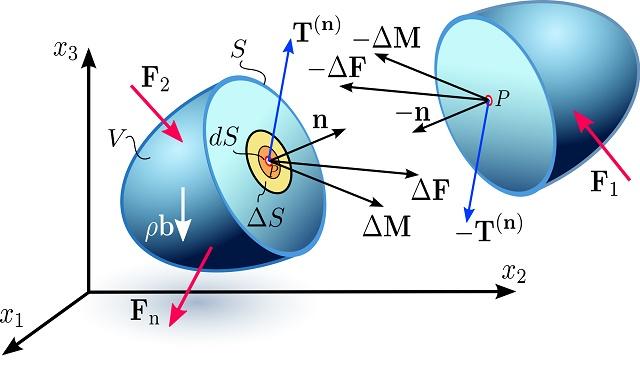
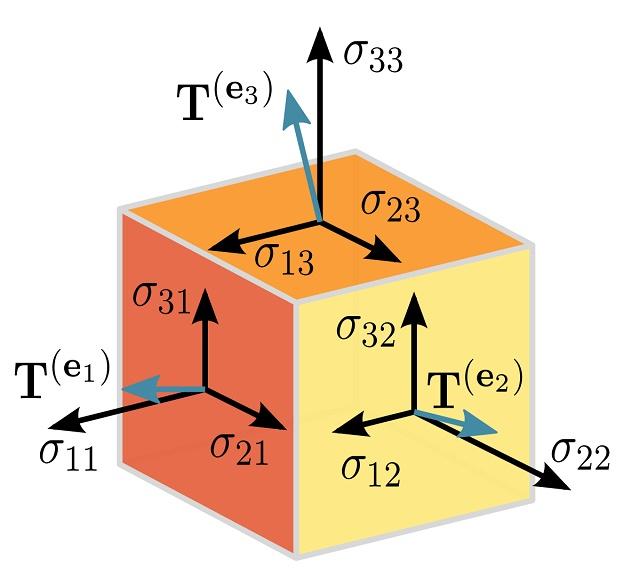
- بردار تنش
- تانسور تنش
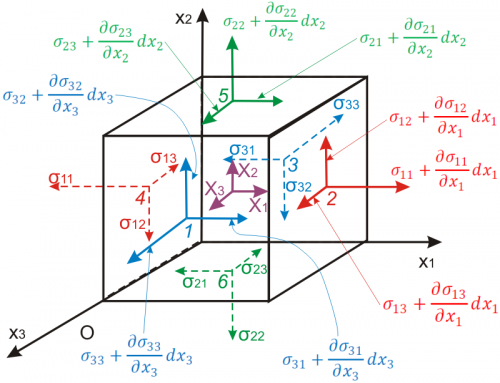
- مولفه هاي تانسور تنش
- تقارن تانسور تنش، اصل ممان اندازه حركت
- تنش هاي اصلي
- تنش برشي حداكثر
- معادلات حركت، اصل اندازه حركت خطي
- شرط مرزي براي تانسور تنش
- مسائل
فصل 5: جامد الاستيك خطي
- خواص مكانيكي
- جامد الاستيك خطي
- جامد الاستيك همسانگرد خطي
- مدول يانگ، ضريب پواسون، مدول برشي و مدول حجمي
- معادلات نظريه بي نهايت كوچك الاستيسيته
- اصل جمع آثار
- مثال هاي از الاستو ديناميك
- موج غير چرخشي مسطح
- موج هم حجم مسطح
- انعكاس امواج الاستيك مسطح
- ارتعاش يك ورق بي نهايت
- مثال هايي از الاستو استاتيك
- كشش ساده
- پيچش يك استوانه مدور
- پيچش يك استوانه غير مدور
- خمش خالص يك تير
- كرنش مسطح
- مسائل
فصل 6: سيال چسبنده نيوتني
- سيالات
- سيالات تراكم پذير و تراكم ناپذير
- معادلات هيدرو استاتيك
- سيال نيوتني
- تفسير لاندا و مو
- سيال نيوتني تراكم ناپذير
- شرايط مرزي
- خط جريان، خط مسير، جريان پايدار و ناپايدار، جريان لايه لايه و مغشوش
- مثال هاي از جريان هاي لايه لايه يك سيال نيوتني تراكم ناپذير
- جريان كوئت مسطح
- جريان پوسله مسطح
- جريان هاگن پوسوله
- جريان كوئت مسطج از دو لايه سيال تراكم ناپذير
- جريان كوئت
- جريان نزديك يك ورق مرتعش
- نرخ كار انجام شده روي يك ذره
- نرخ سيلان حرارت به داخل يك المان
- معادله انرژي
- بردار چرخش
- جريان غير چرخشي
- جريان غير چرخشي يك سيال تراكم ناپذير غير چسبنده با چگالي همگن
- جريان هاي غير چرخشي به عنوان حلي براي معادله ناوير استوكس
- معادله انتقال چرخش براي سيال چسبنده تراكم ناپذير با چگالي ثابت
- مفهوم لايه مرزي
- سيال نيوتني تراكم پذير
- معادله انرزي بر حسب آنتالپي
- موج صوتي
- جريان هاي باروتروپيك و غير چرخشي سيال تراكم پذير غير چسبنده
- جريان يك بعدي يك سيال تراكم پذير
- مسائل
فصل 7: فرمول بندي انتگرالي اصول عمومي
- قضيه گرين
- قضيه ديورژانس
- انتگرال روي يك حجم كنترل و انتگرال روي يك سطح مادي
- اصل بقاي جرم
- اصل مقدار حركت خطي
- پيرامون حجم كنترل متحرك
- اصل ممان اندازه حركت
- اصل بقاي انرژي
- مسائل
فصل 8: سيال ساده تراكم ناپذير
- هيات جاري، به عنوان هيات مرجع
- تانسور تغيير شكل نسبي
- تانسور سابقه تغيير شكل، تانسورهاي رولين اريكسن
- سيال ساده تراكم ناپذير
- سيال رولين اريكسن
- جريان هاي ويسكومتر يك سيال ساده تراكم ناپذير
- تنش ها در جريان ويسكومتر يك سيال ساده تراكم ناپذير
- جريان هاي برشي ساده
- جريان در كنال
- مسائل

كتاب مقدمه اي بر مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته (Introduction to Continuum Mechanics)، مشتمل بر 536 صفحه، در 8 فصل، با فرمت PDF، به زبان انگليسي، همراه با مسائل به ترتيب زير گردآوري شده است:
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Tensors
- Chapter 3: Kinematics of a Continuum
- Chapter 4: Stress and Integral Formulations of General Principles
- Chapter 5: The Elastic Solid
- Chapter 6: Newtonian Viscous Fluid
- Chapter 7: The Reynolds Transport Theorem and Applications
- Chapter 8: Non-Newtonian Fluids

كتاب تشريح كامل مسائل مقدمه اي بر مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته، مشتمل بر 246 صفحه، با فرمت PDF، به زبان انگليسي، كليه مسائل كتاب بالا (Introduction to Continuum Mechanics) را بطور كامل تشريح نموده است.

جهت دانلود مجموعه آموزشي مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته به همراه تشريح كامل مسائل، برلينك زير كليك نماييد.
مقدمه اي بر مكانيك محيط هاي پيوسته به همراه تشريح كامل مسائل










 روش هاي اجزاي محدود
روش هاي اجزاي محدود آموزش مقدماتي تا پيشرفته روش هاي عناصر محدود غير خطي
آموزش مقدماتي تا پيشرفته روش هاي عناصر محدود غير خطي مجموعه آموزش روش هاي اجزاي محدود مقدماتي
مجموعه آموزش روش هاي اجزاي محدود مقدماتي روش اجزاي محدود مقدماتي
روش اجزاي محدود مقدماتي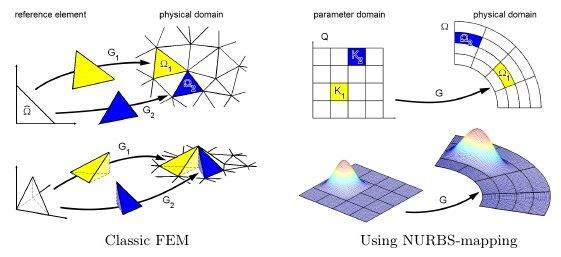 برنامه المان چهار گرهي تنش مسطح و كرنش مسطح در نرم افزار MATLAB
برنامه المان چهار گرهي تنش مسطح و كرنش مسطح در نرم افزار MATLAB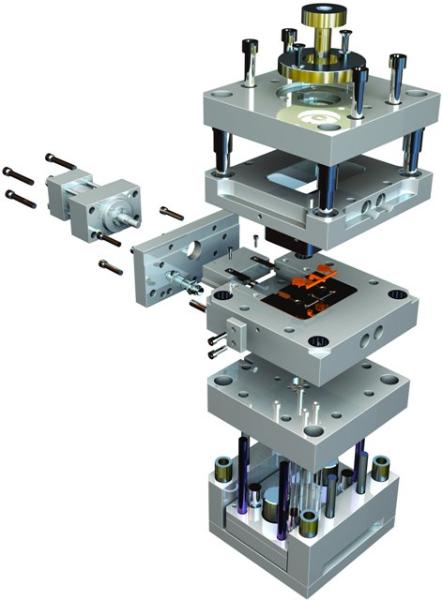 طراحي قالب تزريق پلاستيك (Injection Mold Design)
طراحي قالب تزريق پلاستيك (Injection Mold Design)